Explore 7 methods to Print on Plastic
Printing on plastic is essential for a vast range of applications, from product packaging and labels to promotional items and industrial parts. The right printing method ensures durability, high-quality visuals, and cost-effectiveness. With so many options available, understanding each one is key to making the best choice for your project.This comprehensive guide will explore seven popular methods for printing on plastic, providing you with the knowledge you need to select the perfect solution.
1. Digital InkJet Printing
Digital InkJet printing is a versatile and modern method that uses computer-controlled print heads to spray microscopic droplets of ink directly onto the plastic surface. It’s a non-contact process, meaning the print head never touches the material.
- How it works: Ink is precisely jetted onto the substrate in a pattern defined by a digital file. UV-curable inks are often used, which are instantly cured and hardened by a UV light, ensuring excellent adhesion and durability.
- Best for: Short runs, prototypes, and personalized items. It excels at complex, multi-color designs and variable data printing (e.g., serial numbers, barcodes).
- Advantages: Quick setup, no need for printing plates, and the ability to print high-resolution, full-color images.
- Limitations: Slower for high-volume production and can be more expensive per unit compared to other methods for large quantities.
2. Screen Printing
Screen printing is a traditional and highly durable method that involves pushing ink through a stenciled mesh screen onto the plastic.
- How it works: A fine mesh screen is stretched over a frame. Areas of the design are blocked out, leaving open mesh areas for the ink to pass through. A squeegee is used to press ink through the screen onto the plastic substrate.
- Best for: Flat or relatively flat surfaces, thick ink deposits, and designs requiring high opacity. It’s ideal for signs, decals, and industrial parts.
- Advantages: Produces a thick, tactile layer of ink that is highly durable and resistant to fading, scratching, and chemicals. It can be used on a wide variety of plastic types.
- Limitations: Not ideal for high-detail or complex gradients. Each color requires a separate screen, which increases setup time and cost.
3. Flexographic Printing
Flexographic printing, or Flexo printing, is a high-speed, rotary printing method that uses flexible relief plates to transfer ink onto the plastic. This method is the workhorse of the plastic packaging industry.
- How it works: A flexible plate, typically made of photopolymer, is wrapped around a rotating cylinder. The raised image on the plate is inked by an anilox roller, which delivers a consistent amount of ink. This inked plate then presses against the plastic substrate to create the print. Flexo printing machines are designed for continuous, high-speed operation.
- Best for: High-volume production of flexible plastic packaging, plastic films, bags, labels, and food wraps.
- Advantages: Extremely fast production speeds, low cost per unit for long runs, and the ability to print on non-porous, flexible materials. It works with a range of inks, including water-based inks, solvent-based inks, and UV-curable inks, making it highly adaptable.
- Limitations: High initial setup cost due to the creation of printing plates. It’s less suitable for short runs or complex photographic imagery.
4. UV Litho Printing
UV Litho printing (also known as Offset Printing) uses a printing plate and an intermediate rubber blanket to transfer the image onto the plastic. It’s a high-quality printing process, especially when using UV-curable inks.
- How it works: The design is etched onto a plate. Ink is applied to the image area, and then transferred to a rubber blanket, which in turn presses the image onto the plastic. UV light instantly cures the ink.
- Best for: High-quality, detailed graphics on rigid plastics like PVC, polycarbonate, and acrylic. Common applications include credit cards, ID cards, and lenticular prints.
- Advantages: Exceptional print quality and resolution, excellent color fidelity, and the ability to print fine details and smooth gradients.
- Limitations: Primarily used for rigid plastics. The setup time and cost make it less suitable for small quantities.
5. Pad Printing
Pad printing is an indirect offset method that transfers a 2D image onto a 3D object. It’s ideal for printing on irregular or curved plastic surfaces.
- How it works: An image is etched into a flat plate (cliché). Ink fills the etched area, and a soft silicone pad presses against the plate, picking up the ink. The pad then deforms to conform to the shape of the plastic object, transferring the image.
- Best for: Small, curved, or oddly shaped plastic items like bottle caps, medical devices, electronic casings, and promotional pens.
- Advantages: The unique ability to print on non-flat surfaces. It offers good detail and durability.
- Limitations: Slower than other methods for flat surfaces and generally limited to smaller images and fewer colors.
6. Laser Printing
Laser printing on plastic doesn’t use ink but instead uses a laser beam to create marks or etchings directly on the surface.
- How it works: A high-intensity laser beam changes the color or texture of the plastic material itself. This can be done through foaming, carbonizing, or engraving.
- Best for: Permanent marking, numbering, and coding on plastic components, such as electronic parts and medical instruments. It’s also used for creating barcodes and QR codes.
- Advantages: Highly precise, durable, and permanent. The marks are resistant to abrasion and chemicals. No ink is required, eliminating the need for drying or curing.
- Limitations: Limited to monochrome marks. It’s a marking process rather than a full-color printing method.
7. Hot Stamping
Hot stamping is a dry printing method that uses heat and pressure to transfer a pre-dried ink or foil from a carrier film onto the plastic surface.
- How it works: A heated die with a raised design presses a roll of foil onto the plastic. The heat and pressure cause the foil to release from its carrier and adhere to the plastic surface, creating the impression.
- Best for: Adding metallic, holographic, or matte finishes to plastic products. It’s popular for cosmetic packaging, luxury goods, and security features.
- Advantages: Creates a premium, high-end look and feel. The finish is very durable and vibrant.
- Limitations: Not suitable for multi-color or complex images. It’s a single-color process and can be slower than other methods.
Choosing the Best Method for Your Plastic Printing Needs
Selecting the right printing method is crucial for success. Here’s a quick guide to help you decide:
- For high-volume flexible packaging: Flexographic printing is the clear winner. Its speed and efficiency make it the most cost-effective solution for large-scale production.
- For short runs and custom designs: Digital InkJet printing offers flexibility and high-quality results without the need for expensive setup.
- For durable, thick prints on flat surfaces: Screen printing provides unmatched durability and vibrant colors.
- For irregular or curved objects: Pad printing is the only viable solution for printing on uniquely shaped items.
- For permanent marking and coding: Laser printing creates highly durable, permanent marks without any consumables.
- For premium, metallic finishes: Hot stamping delivers a luxurious, eye-catching result.
Tips for Optimizing Plastic Printing Quality
- Surface Preparation: Ensure the plastic surface is clean and free of dust, grease, or any contaminants. Surface treatments like corona or plasma treatment can improve ink adhesion.
- Ink Compatibility: Always use an ink formulated for the specific type of plastic you are printing on. For example, some inks adhere well to PVC but not to polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP).
- Curing: Proper curing is essential for durability. Whether using UV, solvent, or water-based inks, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure the ink is fully cured and bonded to the substrate.
- Quality Control: Implement rigorous print quality control checks. This includes verifying color accuracy, print registration, and ink adhesion through tests like the tape test.
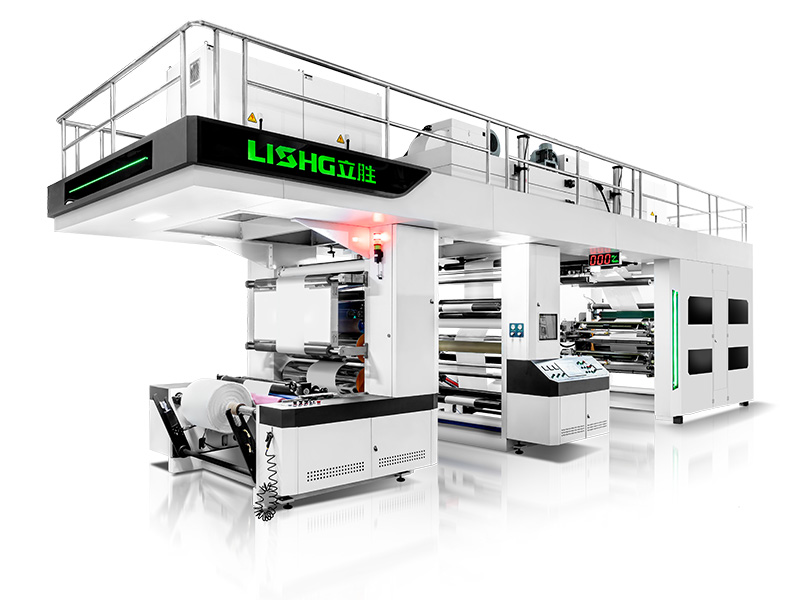
LISHG Printing Solutions for Plastic
At LISHG, we specialize in providing state-of-the-art flexographic printing machines that are ideal for high-speed, high-quality plastic printing. Our machines are designed to meet the demands of modern flexible packaging printing, offering precision and efficiency.
Whether you’re printing on plastic bags, films, or labels, our flexo printing machines on plastic are equipped with advanced features like high-precision tension control, automatic registration systems, and rapid anilox roller changes to minimize downtime and maximize productivity. We can help you achieve superior print quality, from simple designs to complex, multi-color graphics.
Contact us today to learn more about our solutions and how we can help you with your plastic printing needs.
FAQs
What is the best ink for printing on plastic?
The best ink depends on the type of plastic and the printing method. UV-curable inks are popular for their fast curing and excellent adhesion on many non-porous plastics. Solvent-based inks are known for their strong bonding properties and are widely used in flexo printing. For certain applications, specialized water-based inks are also available, offering a more eco-friendly option.
Which method is fastest for high-volume production?
Flexographic printing is by far the fastest method for high-volume plastic printing, capable of running at speeds of hundreds of meters per minute. It is the industry standard for mass production of items like packaging films and labels.
Can flexo printing handle irregular plastic surfaces?
No, flexo printing is best suited for flat or roll-fed flexible plastic films and sheets. For irregular or 3D objects, pad printing is the most effective method.
How to ensure print adhesion on PE or PP?
Polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) are known for their low surface energy, which can make ink adhesion difficult. The most common solution is to treat the surface using a corona treatment or plasma treatment before printing. This process increases the surface energy, allowing the ink to properly wet and bond with the plastic. Using an ink specifically formulated for PE/PP is also essential.